Revenue Recognition Principles, Criteria for Recognizing Revenues

The Cost of Revenue includes direct costs such as raw materials, labor, manufacturing, and production expenses. Each business will have a distinct set of direct costs, which may evolve over time. Accurately tracking these expenses ensures a precise calculation of CoR, reflecting the true cost of producing and delivering goods and services. A post on Profitwell, a publication for software-as-a-service businesses, argues that those who think so aren’t using it correctly. ARPU can be analyzed for insights into customers‘ responses to the company’s various price points and premium offerings. In terms of real estate investments, revenue refers to the income generated by a property, such as rent or parking fees.

What is Revenue Recognition?
The purpose of the principle of revenue recognition is to ensure that a company recognizes revenue in a manner that accurately reflects its financial performance. By following this principle, a company can provide relevant and reliable financial information to its stakeholders, including investors, creditors, and regulators. Accrued revenue (or accrued assets) is an asset such as proceeds from delivery of goods or services. Income is earned at time of delivery, with the related revenue item recognized as accrued revenue.
Revenue vs Income
When this matching is not possible, then the expenses will be treated as period costs. This means revenue is not recognized upfront at the time of the sale for the entire subscription fee but rather over the course of the subscription period. In other words, according to the realization principle, revenue can only be recognized once earned. This principle helps public and private companies align their accounting practices with the revenue recognition principle to achieve accurate financial reporting. The tax implications of realization accounting are profound, influencing how businesses report income and manage their tax liabilities.
Intro to Revenue Recognition: GAAP Principles
- To increase profit, and hence earnings per share (EPS) for its shareholders, a company increases revenues and/or reduces expenses.
- Beneath that are all operating expenses, which are deducted to arrive at Operating Income, also sometimes referred to as Earnings Before Interest and Taxes (EBIT).
- However, revenue growth can be even more important than the revenue number itself.
- By following this principle, a company can provide relevant and reliable financial information to its stakeholders, including investors, creditors, and regulators.
- Revenue and income are often confused because they are both financial terms that refer to money coming into a company.
When public companies report their quarterly earnings, two figures that receive a lot of attention are revenues and EPS. A company beating or missing analysts‘ revenue and earnings per share expectations can often move a stock’s price. Revenue realization and revenue recognition are unique but related concepts. Learn the difference between them and how each impacts your business’s ability to accurately forecast revenue and measure true earnings.
- Based on the revenue recognition principle, the revenue is recognized on July 1 because that is when the service was provided – when the bike repair took place.
- While revenue is a gross amount focused just on the collection of proceeds, income or profit reports the net proceeds.
- It is important to note that accrued and deferred revenue does not exist under the cash basis accounting.
- Accurately tracking these expenses ensures a precise calculation of CoR, reflecting the true cost of producing and delivering goods and services.
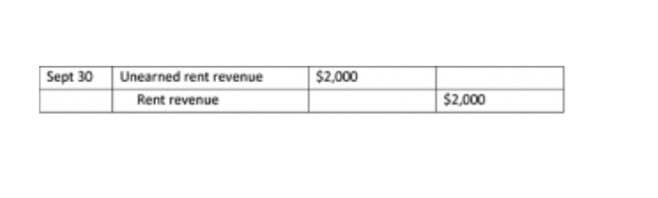
Accrued and Deferred Revenue
One such technique is the use of percentage-of-completion accounting, particularly relevant for long-term projects like construction. This method allows companies to recognize revenue and expenses proportionally as the project progresses, rather than waiting until completion. By doing so, businesses can provide a more accurate representation of their financial performance over the project’s duration.

The articles and research support materials available on this site are educational and are not intended to be investment or tax advice. All such information is provided solely for convenience purposes only and all users thereof should be guided accordingly. Finance Strategists has an advertising relationship with some of the companies included on this website. realization of revenue definition accounting We may earn a commission when you click on a link or make a purchase through the links on our site. All of our content is based on objective analysis, and the opinions are our own. CFI’s e-Commerce Financial Modeling Course provides a detailed breakdown of how to build this type of model, which is extremely important for forecasting and business valuation.
Revenue Realization vs Revenue Recognition: What’s the Difference?
- The installment method recognizes revenue when payments are received from the customer over time.
- Plus, there is more consistency and comparability between different companies and industries.
- There are different types of revenue, such as operating revenue and non-operating revenue.
- Finally, it also builds trust and adds credibility to financial reporting, which is essential for the stability and growth of financial markets.
- Revenue is the money earned by a company obtained primarily from the sale of its products or services to customers.
They cannot recognize revenue until the client receives what they pay for. For example, if a client signs up for an annual subscription from your SaaS business, you need to see out the year and deliver the software service in full before declaring the sale as earned revenue. Revenue realization plays a critical role in accurate revenue and profit reporting. If sales bookings are reported as revenue, you run the risk of overreporting revenue and making business decisions on an inaccurate cash flow assessment. The fourth criterion for revenue recognition is the assurance of collectability. The company must assess the probability of receiving the consideration it’s entitled to receive under the contract.
Generally accepted accounting principles require that revenues are recognized according to the revenue recognition principle, which is a feature of accrual accounting. This means that revenue is recognized on the income statement in the period when realized https://www.bookstime.com/articles/depreciation-tax-shield and earned—not necessarily when cash is received. While the revenue recognition principle provides a framework for recognizing revenue in a company’s financial statements, there are several challenges that companies may face in applying this principle.
For one, the principle and its corresponding ASC 606 framework give CFOs and accounting teams the tools to accurately portray their companies’ financial performance and health. According to the realization principle, revenues are not recognized unless they are realized. For example, revenue is realized when goods are delivered to customers, not when the contract is signed to deliver the goods. This principle states that profit is realized when goods are transferred to the buyer. Furthermore, revenue should be recognized when goods are sold or services are rendered, whether cash is received or not.


Hinterlasse einen Kommentar
An der Diskussion beteiligen?Hinterlasse uns deinen Kommentar!